- Precision Care for a Stronger Spine
- +91-9619100123
+91-9619100123 | +91-9619200123 | +91-9619300123
spineclinicmumbai@gmail.com
Ankylosing Spondylitis
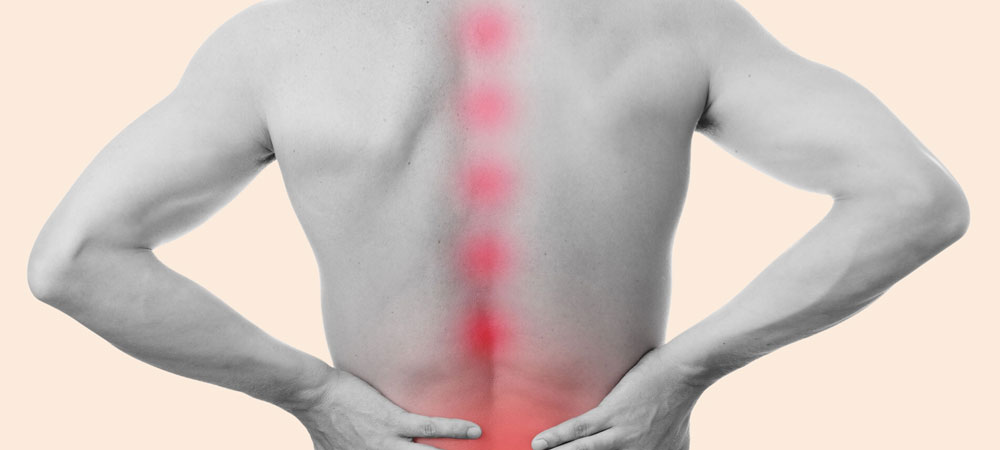
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment in Mumbai
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a kind of arthritis that majorly affects the spine, leading to inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Over time, this chronic inflammation can cause some of the tiny bones in the spine (vertebrae) to fuse, resulting in a loss of flexibility and a hunched-forward posture. In severe cases, the rib cage can also become affected, making it difficult to breathe deeply.
The exact reason for AS is not fully understood till date, but it is believed to be influenced by genetic and environmental factors. The HLA-B27 gene is strongly associated with an increased risk of developing AS, although not everyone with this gene will develop the condition. Symptoms usually begin in early adulthood and may include stubborn pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. The condition can also affect other body parts, including the eyes, heart, and lungs.
Managing AS involves a combination of medications to alleviate inflammation and manage pain, physical therapy to maintain flexibility, and lifestyle changes to support overall health. In some severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct severe deformities. While there is no cure for AS, early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
