- Precision Care for a Stronger Spine
- +91-9619100123
+91-9619100123 | +91-9619200123 | +91-9619300123
spineclinicmumbai@gmail.com
Herniated Disc
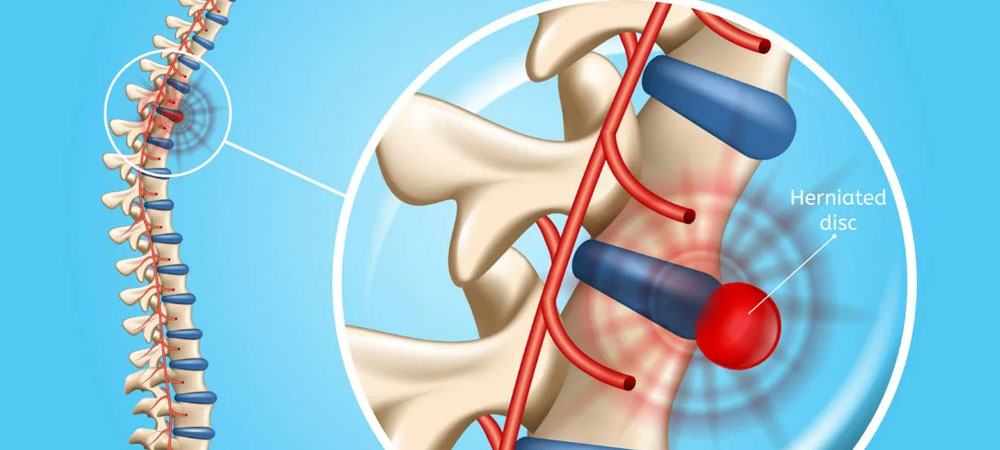
Herniated Disc Treatment in Mumbai
Herniated Disc is a condition where the inner material of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior. This can irritate nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs. Based on the location of the herniation, it can cause symptoms in many parts of the body, like the lower back, legs, or arms.
The exact cause of a herniated disc can vary; it may result from age-related wear and tear (disc degeneration), sudden trauma, or repetitive strain. In some cases, lifting heavy objects incorrectly can lead to disc herniation. While some people experience severe symptoms, others may have no symptoms at all, and the condition might be discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other issues.
Managing a herniated disc typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and pain relief medications. In cases where symptoms persist or worsen, more aggressive treatments such as corticosteroid injections or even surgery may be required. Although most people recover from a herniated disc with conservative treatment, early diagnosis and appropriate management can improve results and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
