- Precision Care for a Stronger Spine
- +91-9619100123
+91-9619100123 | +91-9619200123 | +91-9619300123
spineclinicmumbai@gmail.com
Common Spinal Stenosis Questions
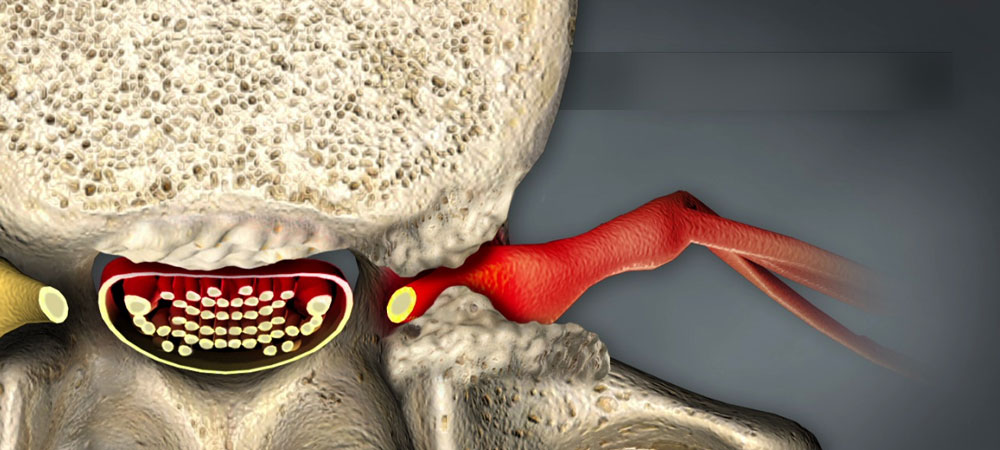
What is Spinal Stenosis?
Spinal stenosis is a disorder where the spaces within the spine narrow, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition commonly affects the neck and lower back (lumbar stenosis), leading to symptoms like pain, numbness, and weakness.
What are the Symptoms?
Symptoms vary based on the position and severity of the stenosis. In the lumbar region, symptoms might include lower back pain, leg pain, and difficulty walking. Cervical stenosis can cause neck pain, balance problems, and even bladder or bowel dysfunction in severe cases.
What Causes Spinal Stenosis?
The most common cause is osteoarthritis, which causes gradual wear and tear of spinal discs and joints. Other causes include herniated discs, thickened ligaments, spinal injuries, and congenital spinal deformities.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult a specialist if you experience persistent back or neck pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness in the limbs. Immediate medical attention is necessary if you have trouble walking, loss of bladder or bowel control, or severe, sudden pain.
How is Spinal Stenosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough extensive physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. These help to identify the location and extent of the stenosis.
What are the Treatment Options?
Treatment varies based on severity. Conservative options include physical therapy, medications, and steroid injections. In more severe cases, surgery like laminectomy or spinal fusion might be recommended.
Can Spinal Stenosis be Prevented?
While it may not be entirely preventable, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and practicing good posture can reduce the risk of developing spinal stenosis. Regular check-ups can also help catch the condition early.
